Over molding is an innovative manufacturing technique that combines two materials into a single part. This process enhances product performance and adds aesthetic appeal. It allows manufacturers to create complex shapes and improve functionality.
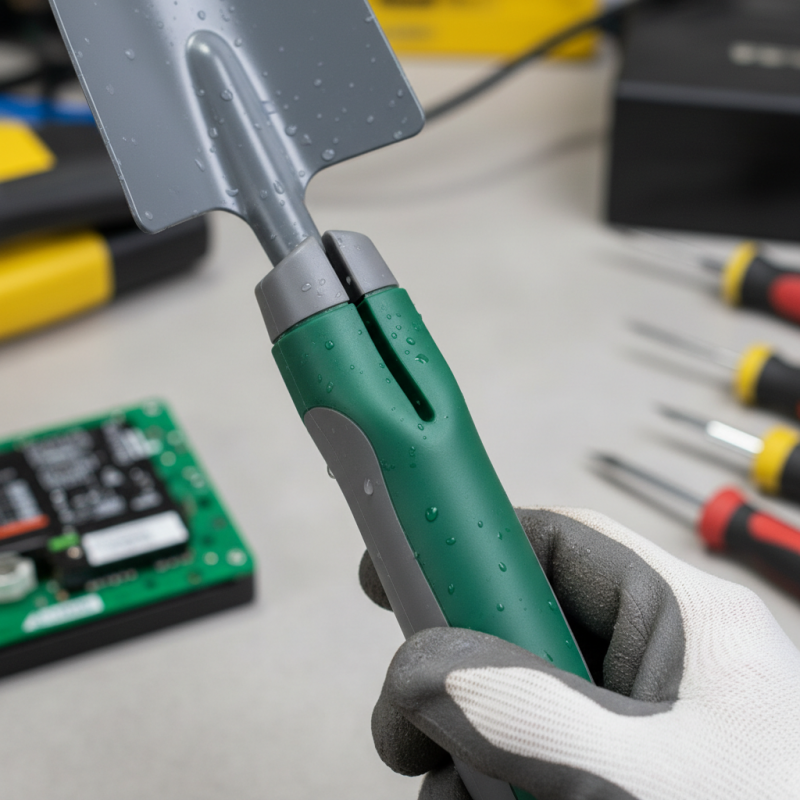
The benefits of over molding are numerous. It can enhance grip on tools and improve durability in harsh environments. Consider the rubber over molding on a hard plastic handle. This functional design increases comfort and safety for users. However, achieving quality results isn't always straightforward. Proper material selection and mold design are crucial.
While over molding offers many advantages, challenges remain. Variations in material bonding can lead to defects. Attention to these details is essential. Each project may require unique solutions. Adapting techniques to specific needs will guide success in over molding applications.

Overmolding is a unique manufacturing technique that combines two or more materials into one product. This process is widely used in producing items like handles, grips, and medical devices. By layering materials, manufacturers can enhance grip, improve aesthetics, and increase durability. The technique allows for creative combinations that can address specific needs.
One popular method in overmolding is inserting a rigid core into a softer, more flexible polymer. For example, rubber can be molded over a hard plastic base to create a comfortable handle. This synergy improves the user experience while maintaining structural integrity. However, understanding the right materials is crucial. Incorrect combinations might lead to adhesion issues.
Designing for overmolding comes with challenges. Manufacturers must account for shrinkage, temperature variations, and material interactions. Miscalculations can result in defects that are costly to fix. Despite these hurdles, careful planning and testing can yield products that stand out in the market. Overall, overmolding opens doors to innovative product designs while posing some risks that require attention.

Overmolding is a process that combines two or more materials to create a single component. The effectiveness of this technique greatly depends on the choice of materials. Common materials used in overmolding include thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers. Each material offers specific benefits tailored for different applications.
Thermoplastics, such as ABS and polycarbonate, are user-friendly. They can be easily processed and reformed. Additionally, they exhibit excellent impact resistance, making them ideal for consumer electronics. On the other hand, elastomers provide flexibility and grip. Materials like TPE (thermoplastic elastomer) are favored for products requiring soft-touch surfaces. Reports indicate that the global thermoplastic elastomer market was valued at over $20 billion in 2021, highlighting their widespread use.
Tips: When selecting materials, consider the end-user experience. Examine the durability and feel of the final product. Moreover, ensure compatibility between materials to prevent delamination. Not all combinations yield successful results. Manufacturers often face challenges in achieving perfect bonds, leading to issues like peeling or separation over time. Testing prototypes can help in identifying potential failures before mass production, fostering better outcomes.
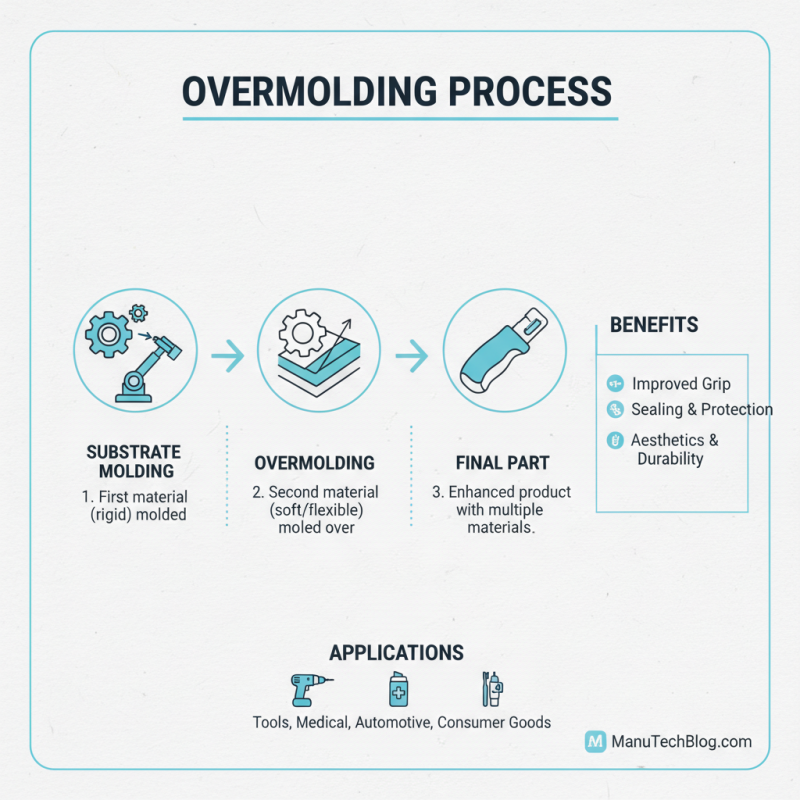
Overmolding is a popular manufacturing process. It involves combining two or more materials to create a single part. This technique enhances product performance and aesthetics. The overmolding process is especially beneficial in creating soft-touch grips or seals.
The first step in overmolding is material selection. Choose the right base material. A common choice is plastic, often used with rubber or silicone. These combinations provide texture and flexibility. The second step involves mold design. The mold must accommodate both materials. Proper alignment is crucial. A misalignment can lead to weak bonds, affecting product durability.
During the injection process, consider temperature settings carefully. The base material’s temperature should be precise to achieve optimal adhesion. Reports indicate that a well-executed overmolding process can increase product lifespan by up to 30%.
Tips: Always perform a test run. This helps identify potential issues before full production. Monitor the cooling cycles closely. Uneven cooling can cause defects. Emphasize quality checks at each stage to minimize errors. Addressing challenges early is key to success in overmolding.
Overmolding is transforming manufacturing processes. This technique allows for creating complex parts by combining different materials. One of the most significant benefits is improved comfort and grip. For instance, in the consumer electronics sector, overmolding can enhance handheld devices. A report from Smithers noted that overmolding can reduce assembly times by up to 50%. This not only saves costs but also improves product quality.
Another key advantage is the reduction in part count. By integrating components, manufacturers simplify designs. This can lead to fewer points of failure in products. The market for overmolded products is expected to grow by 5-7% annually, according to Grand View Research. However, some challenges remain. Not all materials bond well, which can lead to defects. Testing different materials is crucial but often overlooked. This oversight can affect the overall effectiveness of the overmolding process.
The aesthetic appeal is also noteworthy. Overmolding allows for vibrant colors and textures. But achieving the desired look requires a deep understanding of the materials used. Poor material selection can lead to discoloration or texture issues. Manufacturers must consider these aspects to fully realize the benefits of overmolding.
| Technique | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Insert Overmolding | Enhanced strength, reduced assembly time | Automotive components, electronic housings |
| Two-Shot Overmolding | Improved aesthetics, diverse material properties | Consumer electronics, medical devices |
| Overmolding with Soft Thermoplastics | Enhanced grip, comfort, and shock absorption | Handheld tools, sports equipment |
| Shielded Overmolding | Electromagnetic interference protection, durability | Telecommunications, medical electronics |
| Multi-Material Overmolding | Versatile properties, cost-effective | Automotive interiors, wearable technology |
Overmolding is a versatile process used across various industries. It allows for combining two materials into a single piece. This technique enhances product functionality and improves grip and aesthetics. Common applications can be found in electronics, medical devices, and automotive parts.
In the electronics sector, overmolding is often applied to create durable housings. This protects sensitive components from external elements. For instance, a remote control might feature a soft-touch grip for comfort. However, sometimes the materials don’t bond correctly, leading to failures. Proper alignment and material choices are crucial for success.
In medical devices, overmolding is used for enhanced hygiene and easier cleaning. Surgical instruments often have overmolded grips. This provides better control in critical situations. Yet, maintaining consistency in production can be challenging. Variations in temperature during the molding process can affect the outcome. These elements highlight both the potential and the pitfalls of overmolding techniques in real-world applications.